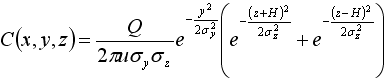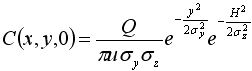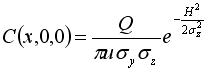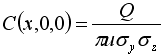Atmospheric Dispersion Calculator
Air Pollution Control Stacks Equation Formulas
Problem:
Solve for plume rise for superadiabatic conditions.
Enter Calculator Inputs:
Can you share this page? Because, it could help others.
Solution:
Solution In Other Units:
Input Unit Conversions:
Change Equation or Formulas:
Tap or click to solve for a different unknown or equation
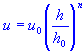 | wind speed at elevation |
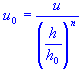 | weather station wind speed |
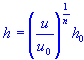 | elevation |
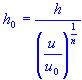 | weather station elevation |
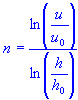 | stability parameter |
| effective stack height | |
| physical stack height | |
| plume rise |
| plume rise | |
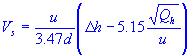 | stack gas exit speed |
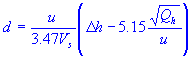 | stack diameter |
| average wind speed | |
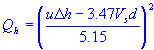 | stack heat emission rate |
| plume rise | |
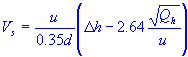 | stack gas exit speed |
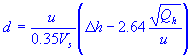 | stack diameter |
| average wind speed | |
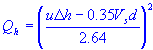 | stack heat emission rate |
| plume rise | |
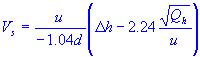 | stack gas exit speed |
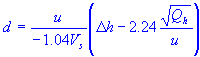 | stack diameter |
| average wind speed | |
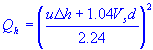 | stack heat emission rate |
| C | = | downwind concentration |
| Q | = | pollution source emission rate |
| u | = | average wind speed |
| σy | = | y direction plume standard deviation |
| σz | = | z direction plume standard deviation |
| x | = | position in the x direction or downwind direction |
| y | = | position in the y direction |
| z | = | position in the z direction |
| H | = | effective stack height |
References - Books:
P. Aarne Vesilind, J. Jeffrey Peirce and Ruth F. Weiner. 1994. Environmental Engineering. Butterworth Heinemann. 3rd ed.
Online Web Apps, Rich Internet Application, Technical Tools, Specifications, How to Guides, Training, Applications, Examples, Tutorials, Reviews, Answers, Test Review Resources, Analysis, Homework Solutions, Worksheets, Help, Data and Information for Engineers, Technicians, Teachers, Tutors, Researchers, K-12 Education, College and High School Students, Science Fair Projects and Scientists
By Jimmy Raymond
![]()
Contact: aj@ajdesigner.com
Privacy Policy, Disclaimer and Terms
Copyright 2002-2015